 Clinically reviewed by Liz Marsh
Clinically reviewed by Liz Marsh
MRI Clinical Lead
Can I Request an MRI? Understanding Your Options
MRI or magnetic resonance imaging is a powerful medical imaging tool. It creates detailed images of the inside of your body to help diagnose diseases and injuries, and check your health. If you’re wondering, “can I just ask for an MRI?”, the answer is yes.
As MRI doesn’t use any radiation, you can self-refer for a private MRI scan if you’re worried about unexplained symptoms or want the peace of mind of knowing where you stand with your health. You don’t always need to get a GP referral.
Here, we’ll take a deeper look at why you might want an MRI scan, how this type of scan works and what it can detect.
How does magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) work?
MRI uses strong magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of the inside of your body in 2D/3D. It works because all the tissues in your body contain water. A small part of these water molecules, called protons, are used by MRI to create images of your different tissues.
Magnetic resonance imaging equipment includes a patient table, the MRI machine and a computer. The MRI machine is made up of a big tube containing powerful magnets and coils that produce radio waves.
During your scan, you will lie down on the patient table. The table will be moved into the tube of the MRI scanner. The tube creates a magnetic field around your body, which lines up all the protons in the water contained in your tissues.
Next, the MRI machine releases gentle pulses of radio waves that make the protons go out of alignment. When the pulses stop, the protons line back up again. This process releases energy signals that are detected by the MRI scanner.
The signals are then sent to a computer to create grayscale images of one cross-section of the inside of your body. More images of cross-sections of your body are created, and these scan images can be processed to form one very detailed 3D image.
The amount of water in tissues in the body determines how bright/dark they show up on an MRI scan. These shades of grey enable us to differentiate between different tissues.
Most soft tissues are varying shades of grey depending on how much water they contain. This allows MRI to detect very subtle differences between tissues, and within tissues, to pick up the early signs of medical conditions.
Comparing MRI to other scan types
MRI provides higher resolution images than ultrasound scans, which use sound waves to create live images of the inside of your body. However, ultrasound scans are faster than MRI scans and don’t need you to stay still for as long.
Another type of scan that produces high-resolution images is a CT scan. However, unlike MRI, a CT scan uses ionising radiation in the form of X rays. This means you cannot self-refer for a CT scan and need to speak to a healthcare professional, such as a doctor, to find out if a CT scan is appropriate.
Both MRI and CT (computerised tomography) can produce 2D and 3D images of the inside of your body, while ultrasound produces 2D images.
Reasons doctors recommend MRI scans
A doctor may recommend an MRI scan to investigate the cause of symptoms you’re having (diagnostic scan), to check the progress of a treatment or to help plan a surgery.
You, therefore, might need an MRI scan to investigate your body’s organs or particular systems to help you get a clear diagnosis.
When is it appropriate to have an MRI?
Although MRI is most often used to investigate symptoms, a private MRI scan can also be used as part of a regular medical check-up.
A full body MRI scan package can give you peace of mind if you’re worried about your general health or have a family medical history of particular health conditions, such as cancers, degenerative brain conditions or heart disease.
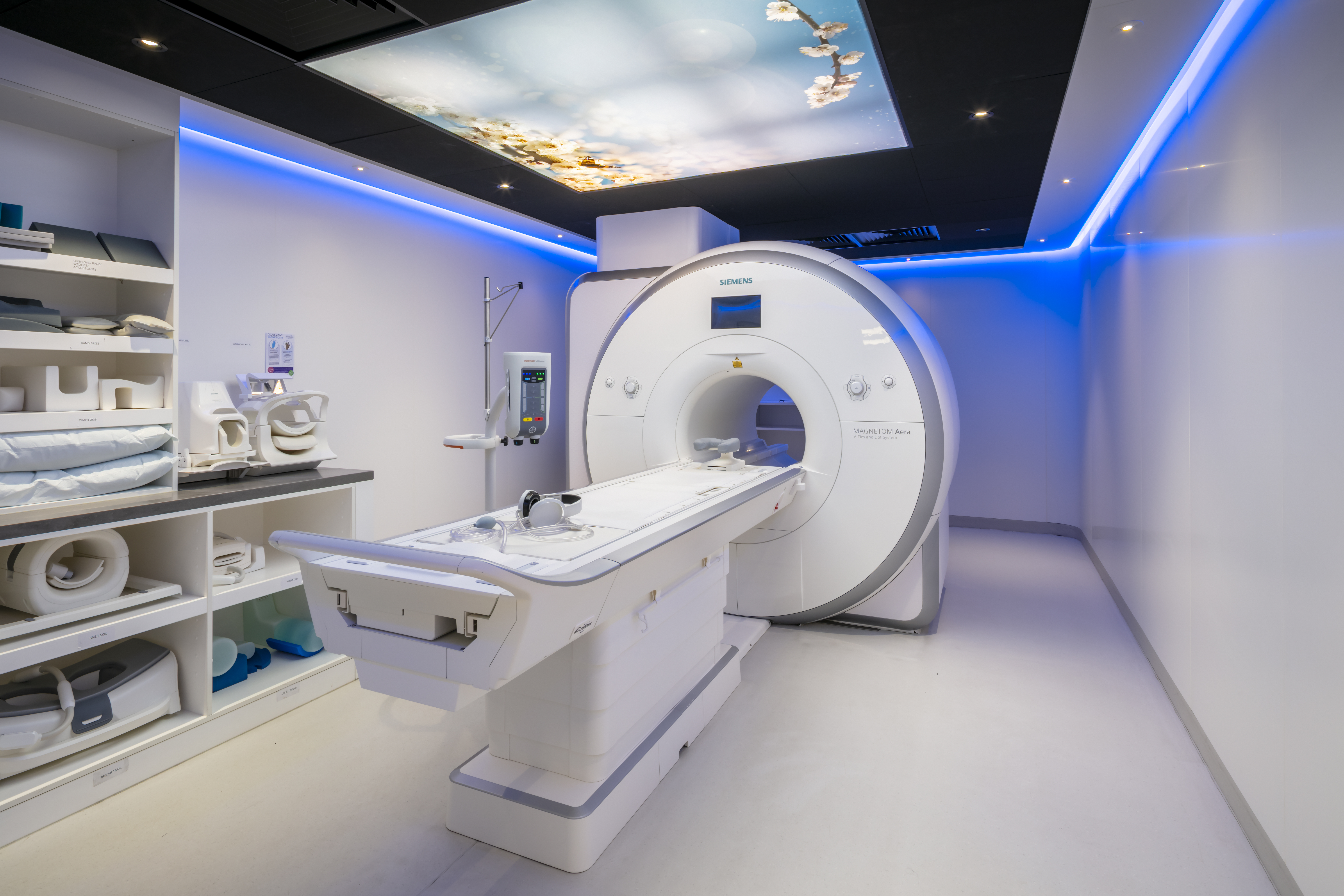
What can MRI detect?
Brain MRI scans
MRI is most commonly associated with brain scans. It can be used to investigate conditions affecting the brain and the spine, which together make up your central nervous system.
It can detect brain tumours, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease and weak, bulging blood vessels that are at risk of bursting (aneurysms). It can also assess damage caused by strokes and head injuries.
Specialised brain MRI scans (functional MRI) can also detect blood flow in the brain to assess how well different parts of your brain are working. This can help plan brain surgery, assess damage from brain conditions such as stroke, and check the effectiveness of treatments.
Cardiac MRI scans
MRI of the heart and its blood vessels can help diagnose heart conditions including heart defects and heart disease. This is because it can create detailed pictures that accurately reveal different aspects of the structures of the heart eg the thickness of the heart wall, overall size of the heart and blockages in blood vessels supplying the heart.
This allows cardiac MRI to detect conditions such as cardiomyopathy, heart valve defects, heart failure and coronary artery disease.
Other MRI scans
An abdominal MRI scan can investigate internal organs within your abdomen including your kidneys, liver, spleen and pancreas, as well as lymph nodes, adrenal glands and the biliary tract.
A kidney MRI scan, also known as renal MRI, can help diagnose kidney disease, renal cancer, kidney cysts and kidney abscesses (eg due to a kidney infection).
A liver MRI scan can help diagnose liver disease, liver cancer, liver cirrhosis and liver cysts.
An abdominal MRI that focuses on the pancreas and biliary tract can help diagnose gallstones and complications from gallstones, such as pancreatitis.
A pelvic MRI scan can investigate the prostate in men and the ovaries, womb and fallopian tubes in women. It can, therefore, help detect cancers of the reproductive organs as well as other conditions affecting these organs, such as an enlarged prostate in men and endometriosis in women.
Visiting a hospital or scanning facility for MRI: what to know
Depending on the MRI scan type you’re having, you may need to have an injection of a special dye called a contrast medium.
If you need to have a contrast agent, your healthcare team will let you know how long you should fast for before your scan. This means you should not eat or drink anything but water for several hours leading up to your scan.
When you arrive for your scan, you’ll be asked to change into a hospital gown and to remove all metal items, such as hair accessories, jewellery, piercings and removable medical devices. This is because metal can interfere with the scan.
Certain metal implants (eg surgical clips) or metal fragments (eg shrapnel) may not be compatible with the MRI machine. If this is the case, your care team will discuss other scan options with you.
You will need to lie very still for your MRI scan as movement can interfere with the clarity of the images created. If you feel nervous about lying down in the tube of the MRI scanner, let your care team know. They can advise you on relaxation techniques and can provide you with special headphones to listen to music during your scan.
While having your scan, there will be a two-way intercom so you can always speak to the Radiographers in your care team who will be in a room adjacent to the scanning room.
The MRI machine will make very loud mechanical noises such as clicking, knocking and banging during your scan. These sounds are part of the normal working process of the machine. You will be given ear protection to reduce the noise.
Once your scan is complete, you can change back into your clothes. Your scan can take up to 90 minutes to complete.
If you have a contrast dye, your care team will ask you to stay at the scanning facility for around 15-30 minutes. This is to check that you don’t develop an allergic reaction to the contrast agent - this happens very rarely and is usually mild and easily treated.
Why choose Vista Health for your MRI?
With our simple self-referral process, you can get fast access to advanced MRI scanning without waiting on a healthcare professional to refer you or dealing with long NHS waiting lists.
You can select from our standard service, with your scan booked in after 7 days, or opt for our fast track service, with your scan booked in within 7 days.
Your scan will be performed by our expert clinical team and we aim to provide a report with your MRI scan results within 3 working days.
Your report will be created by an experienced Consultant Radiologist. You can also discuss your results with one of our highly skilled GPs who will explain what they mean for you. Alternatively, your report can be sent to your NHS GP.
Should you get an MRI scan?
If you have unexplained symptoms, are concerned about your health, or simply want to get expert medical insights so you can stay in good shape for longer, a private MRI scan with Vista Health can help.
Sources
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/mri/about/pac-20384768


